Generic Name:Globin Peptide
METAP®
| 希望小売価格 |
|---|
Introduction
METAP® is a peptide mixture derived from enzyme hydrolysis of globin proteins. Among these peptide, it has been found that the Valine-Valine-Tyrosine-Proline tetrapeptide has strong inhibitory activity on neutral fat elevation.
Furthermore, it has also been found to inhibit the increase blood glucose and of blood pressure.
Was it discovered by ‘a pig that lost weight!?’
At the time, as a feed additive to make pigs effectively gain weight, a hydrolyzed protein was developed. Upon giving the developed feed to pigs, the pigs contrarily lost weight instead of gaining weight.
Thereafter, many studies were conducted to determine the underlying mechanism for the pigs’ weight loss, which led to the creation of the present METAP®.
Effect on Body Fat
Suppression of blood triglyceride elevation (Clinical study)
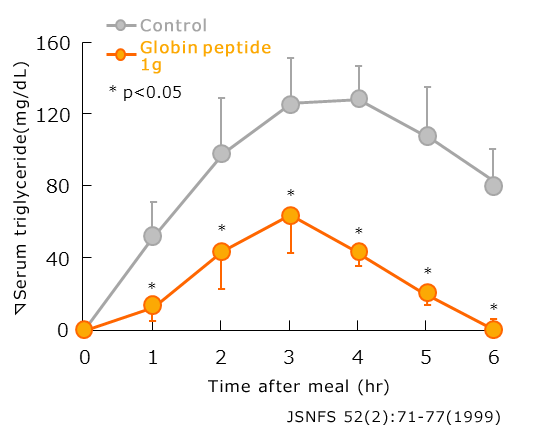
Six test subjects with somewhat high blood neutral fat levels on an empty stomach (blood neutral fat level of 110 – 150 mg/dL) were given either a soft drink containing 1 g of globin peptide, or a placebo, along with a high-fat meal containing 40 g of fat (soup with butter or lard), then the effect on blood neutral fat levels were examined for 6 hours after eating.
Compared to healthy individuals, in the placebo group blood neutral fat levels significantly increased, and did not return to pre-intake levels even 6 hours after meals.
On the other hand, compared to the placebo group, in the globin peptide group the increase in neutral fat level was significantly inhibited at all times. Furthermore, in the globin peptide group, pre-intake levels were restored 6 hours after eating. The area under the curve (AUC) for blood concentrations of the globin peptide group, compared to the placebo group, show that the increase in neutral fat was inhibited by approximately 60 %.
Therefore, we found that globin peptides inhibit the increase in neutral fat.
Furthermore, a similar pattern is seen when remnant-like lipoproteins are measured.
Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase Activity
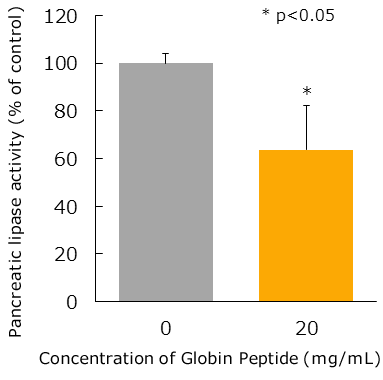
When fat is ingested as part of a meal, pancreatic lipase is secreted in to the duodenum from the pancreas.
This pancreatic lipase works to break down fat into fatty acids and glycerol.
Globin peptide inhibits pancreatic lipase activity, and inhibits the absorption of ingested fat.
The concentration used in trials is based on the intragastric concentration when a human ingests 1 g of globin peptide.
Increase of Lipoprotein lipase activity (In Human)
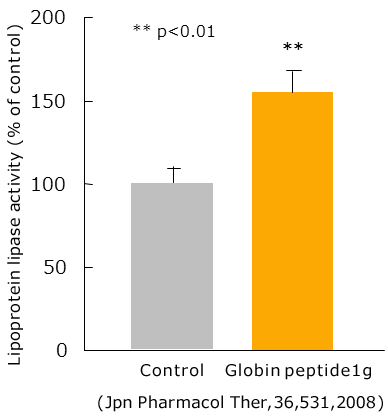
Following meals, blood neutral fat is primarily present in the form of chylomicron, which is a lipoprotein.
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) works to break down neutral fat into free fatty acids and glycerol.
Ten healthy test subjects were given a high fat meal containing 40 g of fat (soup with butter or lard), with a soft drink containing 1 g of globin peptide or a placebo, and the effect on blood LPL activity was examined.
As a result, blood LPL activity was significantly higher in the globin peptide group compared to in the placebo group.
Promotion of Lipid Metabolism (in vitro)
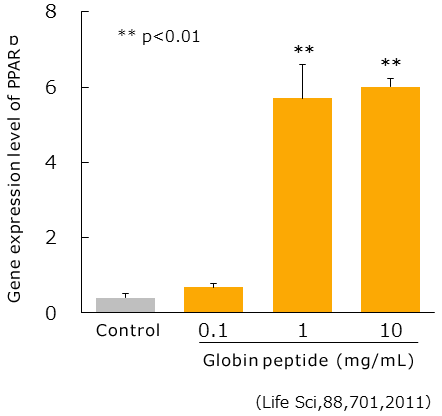
PPAR α is a nuclear receptor that, when activated, promote fatty acid β oxidation, and has been found to promote fatty acid combustion.
Upon adding each concentration of globin peptides to AML-12 hepatic cells, and examining the amount of PPAR α expression after culturing by real time PCR, the amount of PPAR α increased.
Therefore, it is thought that by increasing the amount of PPAR α expression, globin peptides promote fat combustion.
Promotion of Lipid Metabolism (in vivo)
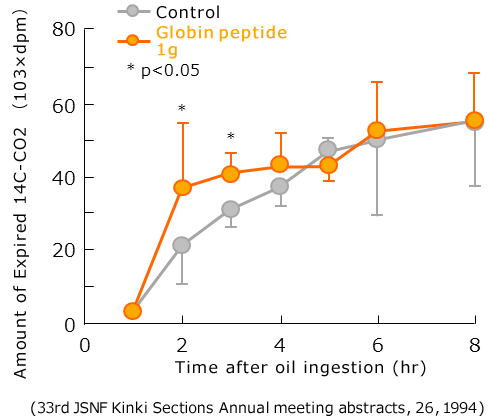
To examine the combustibility of consumed fat to be used as energy, during meals fat is labelled with 14C radioactivity, and the amount of 14C- CO2 respiratory excretion was measured.
Upon giving mice olive oil labelled with 14C radioactivity and globin peptides, it was found that compared to the control group, the amount of 14C CO2 respiratory excretion was significantly increased for 4 hours after administration, and as energy, the fat tended to be easily burnt.
Therefore, it is thought that globin peptides promote fatty acid β oxidation, and promotes fat-burning.
Increase of adipogenesis (in vitro)
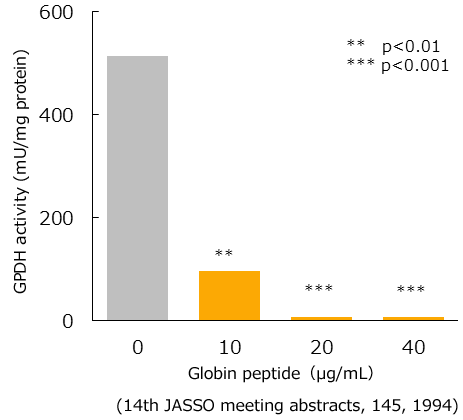
It has been found that when 3T3-L1 fat cells differentiate from precursor cells to mature cells, activity of the enzyme glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH) suddenly increases, and thus GPDH activity has been found to be a marker of fat cell differentiation.
Then, to examine whether globin peptide affected cell differentiation and fat accumulation, GPDH activity was measured using 3T3-L1 fat cells during differentiating from precursor cells to mature cells.
Therefore, it is thought that globin peptides inhibit the accumulation of fat.
Effect To Blood Glucose
Suppression of Blood Glucose Elevation
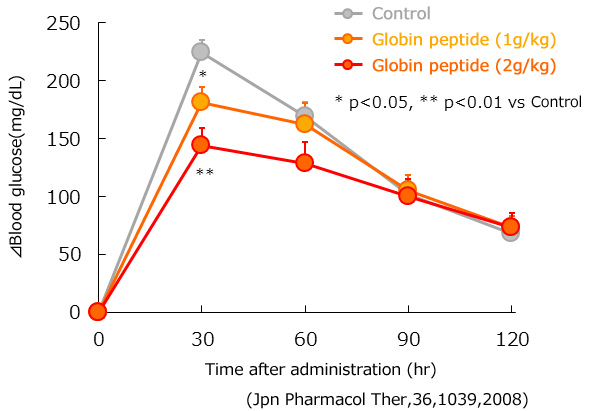
To examine the effect of globin peptides on blood glucose levels, we performed a glucose tolerance test using normal ICR mice.
Upon oral administration of glucose and 1 g or 2 g of globin peptide to mice, at both concentrations the increase in blood glucose levels was significantly inhibited at 30 minutes after glucose loading.
Promotion of glucose uptake (in vivo)
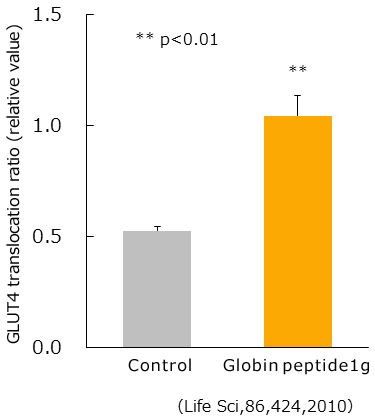
When blood sugar is not incorporated into cells normally, it leads to hyperglycemia, however the sugar transporter GLUT4 plays a key role in maintaining blood glucose levels by way of insulin stimulation. In the absence of insulin stimulation, GLUT 4 accumulates in the cell vesicle, however in the presence of insulin stimulation in the receptors of the cell membrane, GLUT4 is translocated to the cell membrane, and glucose in the blood is transported into the cell.
Therefore, we simultaneously administered 2 g of globin peptide and glucose orally to KKAy mice, which is the type 2 diabetes model, and examined the translocation of Glut 4 to the cell membrane in muscles. As a result, compared to the control group, the globin peptide group exhibited increased translocation of GLUT 4 to the cell membrane.
Thus it is thought that globin peptides promote sugar uptake by GLUT 4, and promotes the use of sugar.
Improvement of Insulin resistance (in vitro)
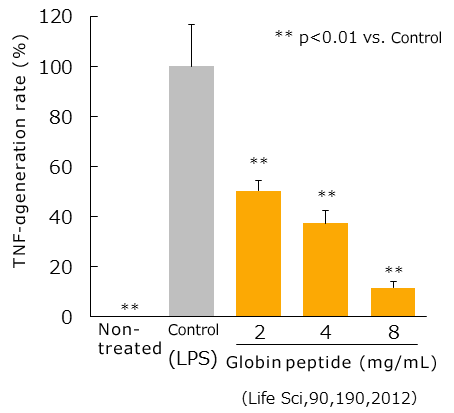
TNF-α works to inhibit insulin signaling, and not only inhibits the expression of GLUT4, which incorporates blood glucose into cells, but also its functioning.
In this way, TNF-α causes insulin resistance, and thus it is important to inhibit the production of TNF-α.
Thus, we examined TNF-α production during LPS stimulation of RAW 264 macrophages.
As a result, when globin peptide was added, TNF-α production was significantly inhibited.
Globin peptide inhibits TNF-α production, and is thus thought to improve insulin resistance.
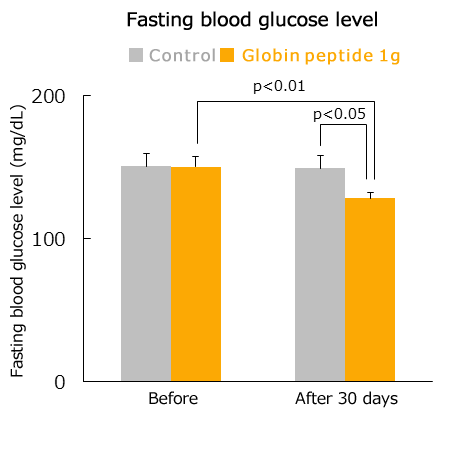
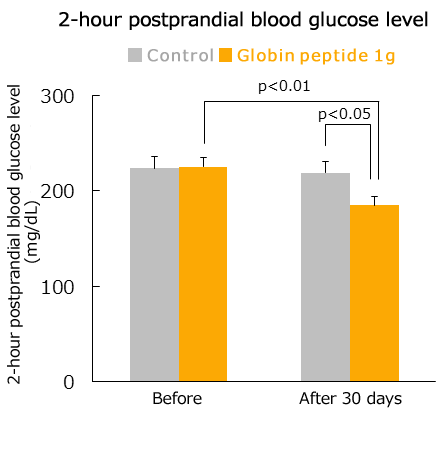
Suppression of blood glucose (in human)
At China’s Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), to examine the effect of globin peptides on patients with type 2 diabetes, 50 test subjects were given either tablets containing 1 g of globin peptide, or a placebo twice a day for 30 days, and the effect on blood glucose levels was examined.
As a result, compared to pre-intake values and the placebo group, the globin peptide group exhibited significantly lower blood glucose levels at fasting. Furthermore, with regards to blood glucose levels at 2 hours after eating, the increase in blood glucose levels was significantly inhibited in the globin peptide group compared to the pre-intake values, and the placebo group.
Moreover, in this human experiment, there were no side effects caused by globin peptide observed.
Effect on Blood Pressure
The effect on blood pressure in single-dose administration (animal experiment)
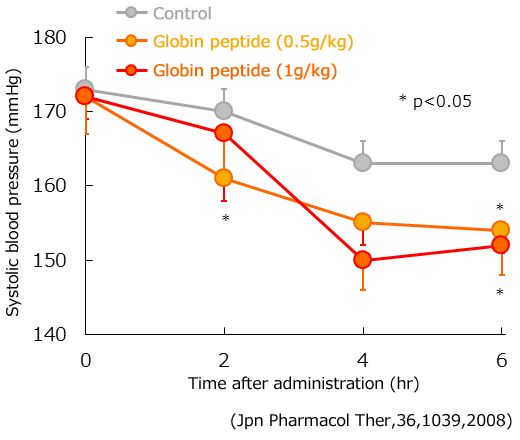
To examine the effect of globin peptide on blood pressure, we conducted an experiment in which spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) were orally administered 0.5 g or 1 g/ kg of globin peptide. As a result, 2 and 6 hours after globin peptide administration, a significant decrease in systolic blood pressure was observed. This blood pressure-lowering effect tended to be somewhat reduced at 8 hours after administration.
Furthermore, in a different trial examine, the effect on blood pressure was examined when normal SD rats were orally administered 1 g/kg of globin peptide, however there was no effect on normal blood pressure observed.
Therefore, globin peptide has no effect on the normal blood pressure, and it was found that blood pressure was lowered when in a hypertensive state.
The effect on blood pressure in repeated administration (animal experiment)
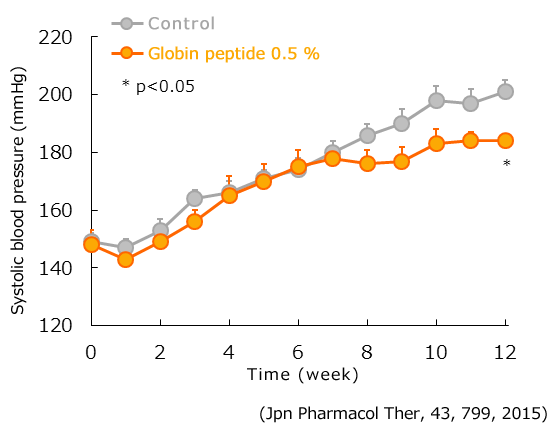
Spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) have accelerated sympathetic nerve function, in conjunction with resistance vessel abnormality, and thus in animals with spontaneous onset of hypertension, as in the control group, blood pressure increases as age in weeks increases.
Upon giving these rats feed containing 0.5 % globin peptide for 12 weeks, blood pressure elevation was inhibited.
Suppression of ACE activity
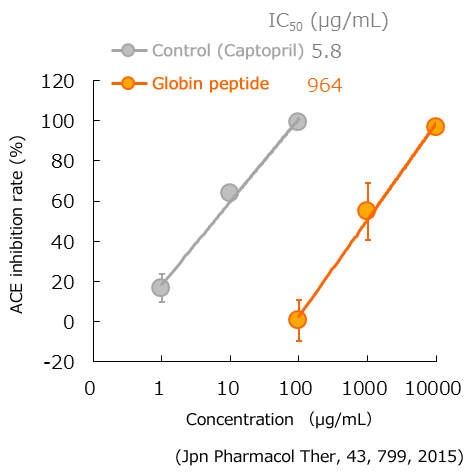
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is an enzyme that converts angiotensin I into II, and angiotensin II is a substance associated with blood pressure elevation. By binding to such receptors, angiotensin II promotes ‘aldosterone secretion’, ‘vascular contraction’, and ‘water and sodium reabsorption’.
Furthermore, aldosterone is a hormone that increases blood pressure, and increases resistance of peripheral blood vessels by way of vascular contraction. Moreover, by promoting water and sodium reabsorption, the volume of blood in the entire body is increased, which leads to increased cardiac output.
Thus, upon examining the effect of globin peptides on ACE activity, globin peptides were found to block ACE activity.
in this way, by inhibiting ACE activity, it is thought that globin peptides inhibit blood pressure elevation.
Safety
Safety
-
Acute toxicity in mice
Mice were given a single oral dose of globin peptide at 10g / kg of body weight and observed for 7 days, however there were no abnormal findings observed.
-
Subacute toxicity in rats
Rats were orally administered globin peptide at a dose of 4 g/ kg/day for 28 consecutive days and observed, however there were no abnormal findings.
-
Mutagenicity
The following 3 types of mutagenicity tests were performed, however there were no abnormalities caused by globin peptide observed.
1) reverse mutation test using bacteria
2) chromosome aberration test using cultivated cells
3) micronucleus test using mice
-
Allergy
Subject blood was examined using the Ouchterlony method, however there were no antibodies to globin peptides observed.
Furthermore, from the globin peptide powder there were no allergens detected that were derived from specific raw ingredients (egg, wheat, milk, buck wheat, peanut, prawn, and crab). (using simple kit to detect food allergens)